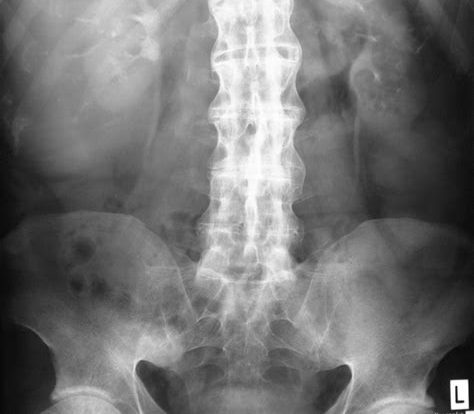
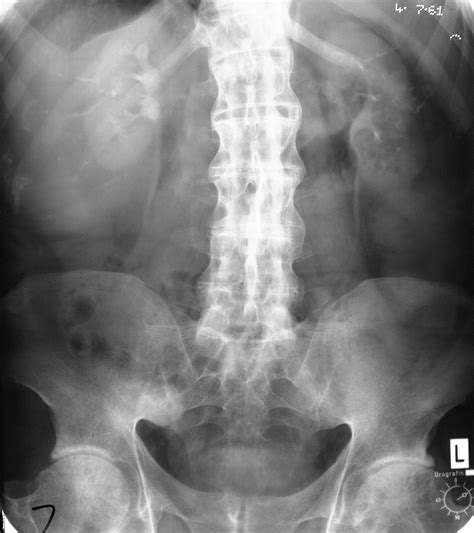
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that affects the spine and can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty moving. Learn more here.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a debilitating condition that affects millions of people around the world. This chronic inflammatory disease primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Despite its prevalence, ankylosing spondylitis remains a relatively unknown condition, often misdiagnosed or overlooked by healthcare professionals. However, recent research has shed new light on the condition, offering hope to those who suffer from its debilitating effects.
Moreover, the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis can be challenging to diagnose, with patients often experiencing pain and stiffness in their lower back and hips for years before seeking medical attention. This delay in diagnosis can lead to irreversible damage to the spine and other joints, making early detection and treatment crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Furthermore, ankylosing spondylitis can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, affecting their ability to work, exercise, and perform everyday activities. As such, raising awareness about this condition is essential to ensure that individuals receive timely and appropriate care.
In conclusion, ankylosing spondylitis is a complex and chronic condition that requires greater recognition and understanding. With ongoing research and improved awareness, we can help those affected by this condition to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Daftar Isi
Introduction
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine. It is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the joints, which can lead to stiffness and pain. The condition can also affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes, heart, and lungs. While there is no cure for AS, there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Back Pain and Stiffness
The most common symptom of AS is back pain and stiffness. This pain is often worse in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and it may improve with exercise or movement. The pain and stiffness can also affect other joints, such as the hips, shoulders, and knees.
Fatigue
People with AS may also experience fatigue, which can be caused by inflammation in the body and the stress of dealing with chronic pain. Fatigue can make it difficult to carry out daily activities and may require extra rest and self-care.
Eye Problems
In some cases, AS can cause inflammation in the eyes, leading to redness, pain, and sensitivity to light. This condition, called uveitis, requires prompt treatment to prevent vision loss.
Breathing Problems
In rare cases, AS can cause inflammation in the lungs, leading to breathing problems. This can be a serious complication that requires medical attention.
Causes of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The exact cause of AS is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. AS tends to run in families, and a specific genetic marker, HLA-B27, is present in many people with the condition. Environmental factors that may trigger AS include infections and exposure to certain toxins.
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
AS can be difficult to diagnose, as there is no single test that can confirm the condition. Doctors may use a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Medications
There are several types of medications that can be used to treat AS, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Biologic drugs, which target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process, may also be used in some cases.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve range of motion, reduce pain, and prevent joint damage in people with AS. Exercises that focus on stretching and strengthening the back, neck, and other affected joints can be particularly beneficial.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding long periods of inactivity can also help manage symptoms of AS and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic condition that can cause significant pain and disability, but with proper treatment and self-care, many people with the condition are able to live full and active lives. If you are experiencing symptoms of AS, it is important to speak with your doctor to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Introduction
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects approximately 0.5-1% of the population worldwide. This condition mostly affects the spine, joints, and other parts of the body, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. AS typically starts in early adulthood and can have a significant impact on daily life.
Causes
The exact cause of AS is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes have been linked to an increased risk of developing the condition, and infections and other environmental triggers may also play a role. The HLA-B27 gene, for example, is present in over 90% of people with AS. However, having the gene does not necessarily mean that a person will develop the condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms of AS include pain and stiffness in the back, hips, and other joints, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Fatigue, loss of appetite, and eye inflammation are also common. Symptoms can vary from person to person and can range in severity. In some cases, people with AS may experience flares, where symptoms worsen for a period of time before getting better.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of AS typically involves a physical exam, blood tests, and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans. A diagnosis may also require ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms. It is important to diagnose AS early, as delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to complications such as fused joints and reduced mobility.
Treatment
Treatment for AS focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing damage to the joints and other affected areas. This can include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), biologics, and physical therapy. Lifestyle changes such as exercise and posture correction can also be beneficial. A multidisciplinary approach involving a rheumatologist, physiotherapist, and occupational therapist is often recommended.
Complications
If left untreated, AS can lead to complications such as fused joints, reduced mobility and flexibility, and chronic pain. In some cases, the condition can also lead to eye inflammation, bowel and bladder problems, and heart and lung issues. Regular monitoring and treatment can help prevent these complications.
Prognosis
The prognosis for AS varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. While there is no cure for AS, timely diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. With proper treatment, many people with AS are able to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Support
Living with AS can be challenging, and support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends can be crucial. Support groups and online forums are also available to help those with AS connect with others who understand their experiences. It is important to seek out support and not feel alone in managing this condition.
Research
Research into new treatments and potential cures for AS is ongoing. Advances in genetic testing and personalized medicine may offer new hope for individuals with AS in the future. Clinical trials are also being conducted to test new treatments and improve our understanding of the condition.
Conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic condition that can have a significant impact on quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends can also play a crucial role in managing the condition. Ongoing research offers hope for new treatments and potentially a cure in the future.Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Comprehensive OverviewAnkylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the spine and other joints in the body. It is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the back and hips, and can lead to spinal fusion and loss of mobility.Pros:1. Early Diagnosis – Early diagnosis and treatment of AS can help prevent or delay complications such as spinal fusion and loss of mobility.2. Medication – There are various medications available to treat AS, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), biologics, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These medications can help reduce inflammation and pain, improve mobility, and prevent joint damage.3. Exercise and Physical Therapy – Regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain and stiffness associated with AS.Cons:1. Misdiagnosis – AS is often misdiagnosed or diagnosed late due to its vague symptoms, which can include back pain, fatigue, and stiffness.2. Side Effects of Medications – Some medications used to treat AS can have side effects such as stomach ulcers, increased risk of infections, and liver damage.3. Impact on Quality of Life – AS can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing chronic pain, reduced mobility, and disability.In conclusion, while AS can be a challenging condition to manage, early diagnosis, proper medical treatment, and regular exercise can help improve symptoms and prevent complications. However, the potential side effects of medication and the impact on quality of life should also be considered when managing this condition.
As we come to the end of this discussion about ankylosing spondylitis, it is important to reiterate the key points that have been highlighted. Firstly, it is a chronic and progressive form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine and can lead to severe pain and stiffness. Secondly, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the disease and preventing complications such as spinal deformities and joint damage.
It is also important to note that ankylosing spondylitis is not a death sentence. With proper management, people living with the condition can lead fulfilling lives. This includes a combination of medication, exercise, and lifestyle changes, as well as regular check-ups with a rheumatologist. Additionally, there are support groups and organizations available that offer valuable resources and information for those affected by ankylosing spondylitis and their loved ones.
In closing, it is imperative that we continue to raise awareness and advocate for better understanding and treatment options for ankylosing spondylitis. By doing so, we can help improve the quality of life for those living with this condition and ultimately work towards finding a cure. Thank you for taking the time to read and learn about this important topic.
Video ankylosing spondylitis
As a journalist, it’s important to provide accurate information about health conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis. Here are some common questions people ask about this condition and their answers:
-
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation and pain. It can also affect other joints and organs in the body.
-
What are the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis?
Common symptoms include back pain and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite.
-
What causes ankylosing spondylitis?
The exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, but genetics are believed to play a role.
-
How is ankylosing spondylitis diagnosed?
A diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis may be made based on symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs.
-
What are the treatments for ankylosing spondylitis?
Treatment may include medications to reduce inflammation and pain, physical therapy, and exercise. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
-
Can ankylosing spondylitis be cured?
There is no cure for ankylosing spondylitis, but early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
It’s important to note that each individual’s experience with ankylosing spondylitis may vary. If you suspect you may have this condition, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.






