The glycemic index diet involves eating foods that have a low glycemic index, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote weight loss.
The glycemic index diet has gained popularity over the years, and for good reason. This unique diet focuses on consuming foods that are low on the glycemic index scale, which measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. But what exactly is the glycemic index and how does it affect our body? To understand this, we must first delve into the science behind it.
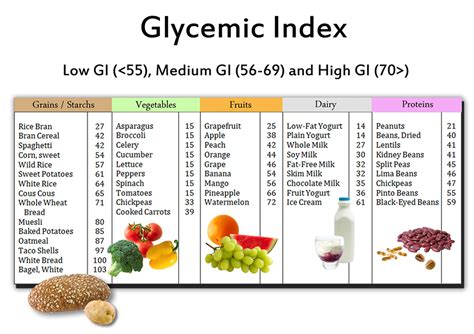
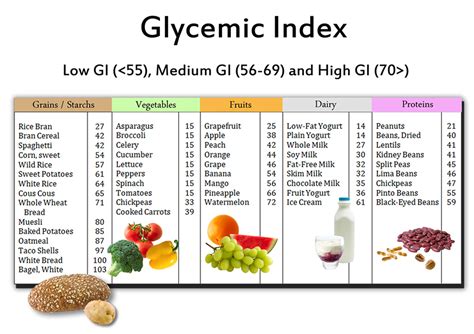
For starters, the glycemic index ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on how much they raise blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose, which has a value of 100. Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) score – such as white bread, rice, and potatoes – cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, leading to a surge of insulin in the body. On the other hand, foods with a low GI score – like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables – are absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream.
But why does this matter? Well, research suggests that following a low GI diet can have numerous health benefits, including better blood sugar control, improved weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. So if you’re looking to revamp your diet and take control of your health, the glycemic index diet may be worth considering.
Daftar Isi
The Glycemic Index Diet: What You Need to Know
If you’re looking for a new way of eating that will help you lose weight and feel healthier, the glycemic index diet may be just what you need. This diet focuses on the types of carbohydrates you eat and how they affect your blood sugar levels. Here’s what you need to know about this popular diet.
What is the glycemic index?
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly carbohydrates in food raise your blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI value are quickly digested and cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while foods with a low GI value are digested more slowly and cause a slower, more gradual increase in blood sugar.
How does the glycemic index diet work?
The glycemic index diet focuses on eating foods that have a low GI value. By doing so, you can help keep your blood sugar levels stable and avoid the spikes and crashes that can lead to overeating and weight gain. The diet also emphasizes eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
What are the benefits of the glycemic index diet?
One of the main benefits of the glycemic index diet is weight loss. Because the diet emphasizes eating low-GI foods that are high in fiber and protein, you’re likely to feel fuller for longer periods of time, which can help you eat less overall. Additionally, the diet may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
What foods should you eat on the glycemic index diet?
Foods with a low GI value include things like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. These foods are high in fiber and other nutrients, and they’re digested more slowly, which helps keep blood sugar levels stable. Foods with a high GI value, on the other hand, include things like white bread, sugary drinks, candy, and processed snacks.
What foods should you avoid on the glycemic index diet?
While there are no strict rules about what you can and can’t eat on the glycemic index diet, it’s generally best to avoid highly processed foods that are high in sugar and refined carbohydrates. This includes things like white bread, pasta, baked goods, and sugary snacks. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients and fiber.
How do you plan meals on the glycemic index diet?
To plan meals on the glycemic index diet, start by focusing on low-GI foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods will help keep blood sugar levels stable and provide a steady source of energy throughout the day. You can also experiment with different types of cooking methods and flavorings to make your meals more interesting and satisfying.
Are there any downsides to the glycemic index diet?
While the glycemic index diet has many benefits, there are some potential downsides to consider. For example, the diet may be difficult to follow if you’re used to eating a lot of processed foods and sugary snacks. Additionally, some people may find that eating only low-GI foods can be too restrictive and may lead to feelings of deprivation or boredom.
Is the glycemic index diet right for you?
Whether or not the glycemic index diet is right for you depends on your individual goals and preferences. If you’re looking for a new way of eating that can help you lose weight, improve your health, and feel more energized, the diet may be worth considering. However, it’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian before making any major changes to your diet.
The bottom line
The glycemic index diet is a popular way of eating that focuses on low-GI foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. By following this diet, you can help keep your blood sugar levels stable, lose weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease. If you’re interested in trying the glycemic index diet, talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian to see if it’s right for you.
Introduction: Understanding the Glycemic Index Diet
The glycemic index diet is a popular nutrition plan that focuses on the effect of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates are an essential source of energy for the body, but certain types can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels. The diet ranks foods based on their glycemic index (GI) value, which measures how quickly they raise blood glucose levels in the body. Understanding the principles behind the glycemic index diet can help individuals make informed decisions about their food choices and promote better health outcomes.
How the Glycemic Index Works
The glycemic index is a scale that ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating foods that cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Foods with a GI value of 70 or above are categorized as high GI, while those with a value of 55 or below are classified as low GI. The GI value of a food is determined by how fast it is broken down into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream. High GI foods are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a spike in blood glucose levels, while low GI foods are digested and absorbed more gradually, leading to a more sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Benefits of a Low-GI Diet
Research suggests that following a low-glycemic index diet may offer several health benefits, such as improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of diabetes, weight loss, improved heart health, and increased satiety. A diet that emphasizes low GI foods can help to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent spikes and crashes that can lead to feelings of fatigue and hunger. It may also help individuals to lose weight by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake. Additionally, consuming a low GI diet has been linked to improved heart health, as it can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Foods to Eat on a Low-GI Diet
Low GI foods include whole-grain bread, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. These foods are rich in fiber, which slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. Consuming a variety of these foods while limiting high GI foods, such as sugary sweets, refined grains, and starchy foods, can help individuals achieve successful weight management and better glycemic control.
Glycemic Index and Exercise
When it comes to exercise, the glycemic index can play a critical role. Consuming low GI foods before workouts can help maintain a stable blood sugar level, facilitating adequate energy to complete the exercise without feeling fatigued. Additionally, consuming high GI foods after exercise can help to replenish glycogen stores in the muscles, promoting recovery and reducing muscle soreness.
Glycemic Load vs. Glycemic Index
Glycemic load (GL) is another factor that people often consider along with the glycemic index. While the glycemic index measures the relative impact of a food on blood glucose levels, the glycemic load considers both the quantity and quality of carbohydrates consumed. For example, a food with a high GI value may have a low GL if it is consumed in small quantities, while a food with a low GI value may have a high GL if it is consumed in large quantities. Therefore, it is important to consider both the GI and GL when making food choices.
Drawbacks of a Low-GI Diet
While a low-glycemic index diet is highly recommended, it may have some drawbacks, such as restrictive food choices, potential for nutrient imbalances, and higher costs with dietary supplement intake making it less feasible for some individuals to adhere to. Some individuals may find it challenging to limit high GI foods, as they may be accustomed to consuming them regularly. Additionally, a low GI diet may not always provide adequate amounts of certain nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin D, which are important for bone health. It may also be more expensive to follow a low GI diet, as many low GI foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, can be more costly than processed foods.
Importance of Consulting a Health Expert
Planning to start a low GI diet? It is essential to consult with a health expert to determine whether it is suitable for you, and get a detailed plan that caters to your nutritional needs, work out, and lifestyle needs. A health expert can help to identify any potential nutrient deficiencies and provide guidance on how to meet your nutritional needs while following a low GI diet. They can also help to tailor the diet to your individual needs, taking into account factors such as your age, sex, activity level, and overall health status.
Does the Glycemic Index Matter for Everyone?
What works for one person does not necessarily work for all. Some individuals may experience a different glycemic response than others due to genetic traits, digestive issues, or medications. It is therefore advisable to consult with a health professional to determine the best diet plan. Additionally, other factors, such as overall calorie intake, physical activity, and stress levels, can also impact blood sugar control and overall health outcomes.
Conclusion: The Bottom Line on the Glycemic Index Diet
The glycemic index diet is an effective and scientifically proven approach for managing blood sugar levels, promoting healthy weight management, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes. However, it is not the only solution. Balancing nutrient content is essential as glycemic index does not consider other important aspects of nutrition like fiber content in foods. It is essential to consult with a health expert to get a personalized plan that best suits you while having a holistic approach to overall lifestyle habits. By making informed food choices, individuals can achieve better health outcomes and improve their quality of life.The Glycemic Index Diet: Sorting Through the Pros and ConsAs a journalist, it’s my role to help readers make informed decisions about their health. One diet that has gained popularity in recent years is the glycemic index diet. Here are some pros and cons to consider before jumping on the bandwagon:Pros:1. Promotes healthy eating: The glycemic index diet emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. This promotes a well-rounded, nutrient-dense diet.2. May improve blood sugar control: By choosing foods with a lower glycemic index, individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance may experience better blood sugar control.3. May aid in weight loss: Choosing low glycemic index foods may help individuals feel more full and satisfied, leading to reduced calorie intake and potential weight loss.Cons:1. Limited evidence: While the concept behind the glycemic index makes sense, there is limited evidence to support its effectiveness in promoting weight loss or improving overall health.2. Can be restrictive: Following a strict glycemic index diet can be challenging, especially when eating out or socializing with others who may not follow the same dietary guidelines.3. Ignores overall nutrition: The focus on the glycemic index of foods may cause individuals to overlook other important factors such as total calorie intake, nutrient density, and overall diet quality.In conclusion, while the glycemic index diet may have some potential benefits, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons before making any dietary changes. As with any diet, it’s essential to prioritize overall health and choose foods that promote a balanced, sustainable lifestyle.
As a journalist, it is important to inform the public about the latest diet trends and how they may affect their health. One such trend is the glycemic index diet, which has gained popularity in recent years. This diet focuses on consuming foods that are low on the glycemic index, which measures how quickly certain foods raise blood sugar levels. While this diet may have some benefits, it is important to approach it with caution and not rely solely on the glycemic index when making food choices.
One potential benefit of the glycemic index diet is that it can help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for those with diabetes or other conditions that affect blood sugar. However, it is important to note that the glycemic index is not the only factor to consider when choosing what to eat. Other factors, such as the overall nutritional value of a food and its calorie content, should also be taken into account. Additionally, some foods that are low on the glycemic index, such as ice cream and chocolate, may not necessarily be healthy choices.
In conclusion, while the glycemic index diet may have some benefits, it should not be relied upon as the sole factor in making food choices. It is important to consider other factors, such as overall nutrition and calorie content, when deciding what to eat. As with any diet, it is also important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your eating habits. By approaching the glycemic index diet with caution and a well-rounded approach, you can make informed decisions about your health and wellbeing.
Video glycemic index diet
Visit VideoPeople Also Ask About Glycemic Index Diet:1. What is a glycemic index diet?
A glycemic index diet is a way of eating that focuses on consuming foods with a lower glycemic index. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index are absorbed more slowly, providing a steady source of energy and helping to control blood sugar levels.
2. What foods can I eat on a glycemic index diet?
Some examples of foods with a low glycemic index include whole grains, nuts, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These foods can be incorporated into meals and snacks to provide sustained energy and promote stable blood sugar levels.
3. What are the benefits of a glycemic index diet?
A glycemic index diet may offer several health benefits, including improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of heart disease, weight loss, and improved energy levels. It may also be helpful for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes.
4. Is a glycemic index diet easy to follow?
While a glycemic index diet can be challenging at first, it can become easier with time and practice. It may require some planning and preparation to ensure that meals and snacks are balanced and include foods with a low glycemic index. However, there are many resources available to help people navigate a glycemic index diet.
5. Can a glycemic index diet be harmful?
For most people, a glycemic index diet is safe and healthy. However, it may not be appropriate for everyone. People with certain medical conditions or dietary restrictions should consult with a healthcare professional before starting a glycemic index diet.






