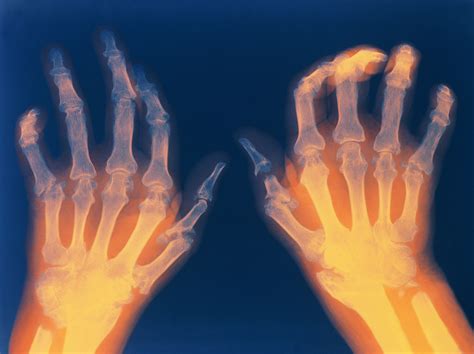
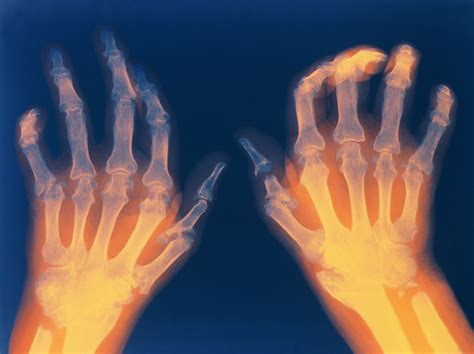
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. Learn more about symptoms and treatment options.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a debilitating condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and difficulty with movement. While there is no known cure for RA, there are various treatments available to manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. However, living with RA can be a challenge, as it not only affects the physical health but also impacts mental and emotional wellbeing. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what rheumatoid arthritis is, what causes it, and how it can be managed.
Daftar Isi
The Basics of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes inflammation and damage to the joints, resulting in pain, stiffness, and swelling. It is estimated that around 1.5 million people in the United States have RA, and it affects women more frequently than men.
The Symptoms of RA
The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person and may come and go over time. Some common symptoms include:
- Joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- Swelling and tenderness in the joints
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and loss of appetite
- Rheumatoid nodules, which are small lumps that form under the skin near affected joints
The Causes of RA
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes may make a person more susceptible to developing RA, and exposure to certain environmental triggers may also play a role.
The Diagnosis of RA
Diagnosing RA can be challenging because the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. To diagnose RA, a doctor will typically perform a physical exam, review the patient’s medical history, and order blood tests to check for certain markers of inflammation.
The Treatment of RA
While there is no cure for RA, there are several treatment options that can help manage the symptoms of the condition and slow its progression. Some common treatments include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow the progression of RA
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and pain
- Biologic drugs that target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow joint damage
- Physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility in the joints
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of RA is crucial for managing the symptoms of the condition and preventing long-term joint damage. If left untreated, RA can lead to permanent joint deformity and disability.
Lifestyle Modifications for People with RA
In addition to medical treatments, there are several lifestyle modifications that people with RA can make to manage their symptoms. Some tips include:
- Getting regular exercise to improve joint mobility and reduce pain
- Eating a healthy diet to maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation
- Avoiding smoking, which can worsen RA symptoms
- Getting plenty of rest to reduce fatigue
Support Resources for People with RA
Living with RA can be challenging, but there are several support resources available to help people manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Some resources include:
- Support groups where people with RA can connect with others who understand their experiences
- Online forums and social media groups for sharing information and support
- Education and advocacy organizations that provide information about RA and resources for managing the condition
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition that can cause significant pain and disability if left untreated. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, people with RA can manage their symptoms and live active, fulfilling lives.
An Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, specifically the synovium, which is the lining of the joints. This leads to inflammation, swelling, and pain in the affected joints. RA commonly affects joints in the hands, feet, and wrists, but it can also affect other parts of the body, such as the lungs, heart, and eyes. RA is a progressive disease that can lead to disability if left untreated.
Symptoms of RA
The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, especially in the morning or after a period of rest. Fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite are also often experienced. RA can cause joint deformities, making it difficult to perform daily tasks such as grasping objects or walking. Other symptoms may include dry eyes and mouth, nodules under the skin, and chest pain when breathing.
Diagnosis of RA
To diagnose RA, doctors will perform a physical exam and review a patient’s medical history. Blood tests will be done to test for markers associated with RA, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans may be used to determine the extent of joint damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent further joint damage and disability.
Treatments for RA
Treatments for RA aim to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and prevent joint damage. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce pain and swelling. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are prescribed to slow the progression of the disease and prevent joint damage. Biologic drugs, which target specific aspects of the immune system, can also be used to treat RA. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may be recommended to improve joint function and mobility. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
Lifestyle Changes for RA
In addition to medication, patients with RA may need to make lifestyle changes to manage their symptoms. Exercise can help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength, but it should be done in moderation and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce inflammation in the body. Rest is also important for those experiencing fatigue. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce pain and improve emotional well-being.
Emotional Impact of RA
Living with RA can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Chronic pain and fatigue can cause depression and anxiety. Many patients with RA may feel isolated and struggle to maintain their usual social activities. It is important for patients to seek support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. Joining support groups can also help patients connect with others who have similar experiences.
RA in Women
RA is more common in women than men, with women being two to three times more likely to develop the disease. Hormonal changes may play a role in this gender disparity. Women who have never given birth or who breastfed for a shorter duration may be at higher risk for developing RA. It is important for women to discuss their reproductive health with their healthcare provider if they have a family history of RA or other autoimmune diseases.
RA in Children
Although it is more common in adults, RA can also occur in children. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) affects children under the age of 16. Symptoms and treatments for JRA are similar to those in adults, but the disease may affect a child’s growth and development. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent long-term joint damage and disability.
New Developments in RA Research
Research on RA is ongoing, with new developments in treatments and therapies being developed. Stem cell therapy, which uses a patient’s own stem cells to repair damaged tissue, is being studied as a potential treatment for RA. Other promising areas of research include gene therapy, personalized medicine, and immunotherapy.
Coping with RA
Although there is currently no cure for RA, there are many ways that patients can cope with their symptoms. Learning stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help patients manage their emotions and reduce pain. Physical therapy and occupational therapy can help improve joint function and mobility. Joining support groups can help patients connect with others who have similar experiences. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that meets their individual needs.Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be a debilitating condition, there are both pros and cons to living with rheumatoid arthritis.Pros:1. Increased awareness: With the growing number of people diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, more attention is being given to this condition. This has led to increased research and funding for better treatments and a potential cure.2. Improved treatments: While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are medications that can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. These treatments have improved over time and continue to advance.3. Support networks: There are many support groups and online communities available for those with rheumatoid arthritis. These networks provide a sense of community and understanding, as well as helpful tips and resources for managing the condition.Cons:1. Chronic pain: Rheumatoid arthritis can cause chronic pain and discomfort in the joints, which can negatively impact quality of life.2. Fatigue: Many people with rheumatoid arthritis experience extreme fatigue, making it difficult to complete daily tasks or work full-time.3. Medication side effects: While medication can help manage symptoms, it can also come with unwanted side effects such as nausea, weight gain, and increased risk of infections.Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, but it is important to focus on the positives and seek out support when needed. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment options, there is hope for a brighter future for those living with this condition.
As a journalist, it is my utmost responsibility to shed light on the different illnesses that are affecting millions of people worldwide. One of these illnesses is Rheumatoid Arthritis. This autoimmune disease affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling, which could lead to a diminished quality of life for those who suffer from it.
It is important to note that Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic illness, meaning that it has no cure. However, there are treatments available that can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in managing this disease, as it can prevent further damage to the joints and organs.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis, such as joint pain and stiffness, fatigue, fever, or weight loss, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. By doing so, you could receive the proper diagnosis and treatment plan that could make a significant difference in your life.
In conclusion, Rheumatoid Arthritis is a serious illness that should not be taken lightly. It is essential to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing them. While there is no cure for this disease, early diagnosis and treatment can improve the quality of life of those who suffer from it. Remember to take care of yourself and your loved ones, and always prioritize your health.
Video rheumatoid arthritis
As a journalist, it’s important to address the questions that people have about certain health conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some of the most common questions people ask about rheumatoid arthritis:
- What is rheumatoid arthritis?
- What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Who is at risk for rheumatoid arthritis?
- How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
- What are the treatments for rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that affects the joints in the body. It causes inflammation in the lining of the joints, which can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness. RA can also cause damage to other organs in the body, such as the heart and lungs.
The symptoms of RA include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, redness, and warmth. These symptoms can occur in any joint in the body, but they most commonly affect the hands, wrists, and feet. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
Anyone can develop RA, but it most commonly affects women between the ages of 30 and 60. Family history, smoking, and obesity are also risk factors for developing RA.
RA is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. A doctor may also perform a joint aspiration, which involves removing fluid from the affected joint to check for inflammation and other signs of RA.
Treatments for RA may include medications, physical therapy, and surgery. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents can help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of RA. Physical therapy can also help improve joint mobility and strength, while surgery may be necessary in severe cases to repair or replace damaged joints.
By addressing these common questions about rheumatoid arthritis, we can help people better understand this condition and how it can be managed. As always, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your health.






