
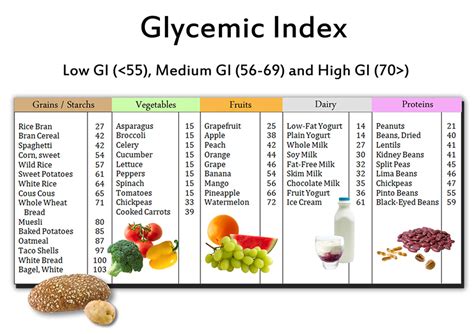
The glycemic index measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood sugar levels. Low GI foods are better for sustained energy levels.
The glycemic index has been a hot topic in the world of nutrition and health for quite some time now. But what exactly is it, and why does it matter? If you’re looking to improve your diet and maintain stable blood sugar levels, understanding the glycemic index is crucial. Simply put, the glycemic index measures how quickly and to what extent a carbohydrate-containing food raises your blood glucose levels. In this article, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of the glycemic index, exploring its impact on your health and wellbeing.
Daftar Isi
Understanding the Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a system used to measure the effect of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. The GI ranks foods based on how quickly they are digested and how much they raise blood glucose levels after consumption. This measurement is especially important for people with diabetes who need to control their blood sugar levels.
What is the Glycemic Index Scale?
The glycemic index scale ranges from 0 to 100. Foods with a high GI value, such as white bread and sugary drinks, are quickly digested and have a rapid effect on blood glucose levels. In contrast, foods with a low GI value, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, are slowly digested and have a gradual effect on blood glucose levels.
Factors Affecting the GI Value of Foods
The GI value of a food can be affected by several factors including the type of carbohydrate, the fiber content, the ripeness of the fruit, the cooking method, and the presence of other macronutrients.
Benefits of Low GI Foods
Low GI foods are beneficial for people with diabetes, as they help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent spikes after eating. Consuming low GI foods can also aid in weight loss, improve satiety, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Limitations of the GI System
Although the GI system is useful for people with diabetes, it has some limitations. The GI value of a food can vary depending on many factors, and it may not reflect the overall nutritional value of a food. Additionally, it does not consider the portion size or the combination of foods consumed together.
Alternatives to the GI System
There are alternative methods to the GI system, including the glycemic load (GL) and the insulin index (II). The GL takes into account both the GI value of a food and the portion size, while the II measures the insulin response to a food rather than the blood glucose response.
How to Incorporate Low GI Foods into Your Diet
To incorporate low GI foods into your diet, focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products. Avoid processed foods and refined carbohydrates such as white bread and sugary drinks. Be sure to also pay attention to portion sizes and combine foods together in a balanced way.
Conclusion
The glycemic index is a useful tool for people with diabetes to regulate blood glucose levels and improve overall health. However, it is important to consider the limitations of the GI system and incorporate a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods into your diet for optimal health.
Introduction to Glycemic Index
Glycemic Index (GI) is a term that has gained popularity in the health and wellness world in recent years. It refers to a measure of how quickly carbohydrate-containing foods raise blood sugar levels. The concept of GI was first developed in the 1980s by Dr. David Jenkins, a professor of nutrition at the University of Toronto. Today, it’s a useful tool for managing diabetes and weight loss diets.
The concept behind Glycemic Index
The GI is based on a scale from 0-100, where 0 represents no effect on blood sugar levels, and 100 represents a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can be problematic for individuals with diabetes, as it can cause a sudden surge in insulin production, which can lead to complications such as diabetic coma. On the other hand, foods with a low GI take longer to digest and absorb, resulting in a slow and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Understanding the effects of different carbohydrates
The GI can be used to rank foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. For example, carbohydrates that break down quickly during digestion and release glucose rapidly into the bloodstream have a high GI. These include foods such as white bread, white rice, and sugary drinks. In contrast, carbohydrates that are digested slowly and release glucose gradually into the bloodstream have a low GI. These include foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Factors that affect Glycemic Index
Several factors can affect the GI of a food, including fiber content, processing, ripeness, and cooking methods. Foods that are high in fiber tend to have a lower GI because fiber slows down digestion and absorption. Processing can also affect the GI of a food, as refined carbohydrates are more easily digested and absorbed than whole grains. The ripeness of a fruit can also affect its GI, as ripe fruits contain more simple sugars than unripe fruits. Finally, cooking methods can affect the GI of a food, as overcooking can break down starches and increase the GI.
Low Glycemic Index foods
Low GI foods are slowly digested and absorbed, producing a slower and lower rise in blood sugar levels. These foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and promote overall health.
Health benefits of consuming low Glycemic Index foods
Consuming low GI foods can provide several health benefits. For individuals with diabetes, low GI foods can improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications such as diabetic coma. Low GI diets have also been shown to reduce insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Additionally, low GI diets have been associated with a reduced risk of developing cardiovascular disease, certain types of cancer, and other chronic conditions.
Glycemic Index and weight management
Low GI diets have been shown to promote weight loss and reduce the risk of obesity. This is because low GI foods can help control appetite and reduce cravings. When we eat high GI foods, our blood sugar levels spike, causing a surge in insulin production. This surge can lead to a rapid drop in blood sugar levels, which can cause us to feel hungry again soon after eating. In contrast, low GI foods provide a slow and steady release of glucose, keeping us feeling fuller for longer.
Glycemic Index and exercise
For athletes and individuals who engage in physical activity, consuming high GI foods before and after exercise can help improve performance and recovery. This is because high GI foods provide a quick source of energy that can be used during exercise. Additionally, consuming high GI foods after exercise can help replenish glycogen stores in the muscles, which can aid in recovery.
Glycemic Index and disease prevention
Low GI diets have been associated with a reduced risk of developing several chronic conditions. In addition to reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, low GI diets have also been shown to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer. Additionally, low GI diets may help improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of depression and other mental health conditions.
Conclusion
Incorporating low GI foods into your diet can provide significant health benefits. By choosing foods that are slowly digested and absorbed, you can stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and promote overall health. Additionally, low GI diets have been shown to promote weight loss and reduce the risk of obesity. Whether you’re managing diabetes, trying to lose weight, or simply looking to improve your overall health, the Glycemic Index is a valuable tool to keep in mind.
The glycemic index is a system that ranks carbohydrates based on their effect on blood sugar levels. The ranking is done on a scale of 0 to 100, with pure glucose having the highest score of 100. Foods with a high glycemic index are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
Pros of Glycemic Index
1. Helps manage blood sugar levels in people with diabetes: People with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels closely, and the glycemic index can help them make informed choices about what to eat. Foods with a low glycemic index are generally better for people with diabetes because they help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
2. May improve heart health: Some studies have shown that following a diet based on the glycemic index can improve heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides in the blood.
3. May aid in weight loss: Foods with a low glycemic index tend to be more filling and can help people feel full for longer periods, reducing the overall number of calories consumed.
Cons of Glycemic Index
1. Not always accurate: The glycemic index is based on the effect of individual foods on blood sugar levels, but the actual effect can vary depending on many factors, including cooking methods, ripeness, and processing.
2. Ignores portion sizes and food combinations: The glycemic index only considers the effect of individual foods and does not take into account how much of a particular food is eaten or what other foods are consumed at the same time. For example, eating a high glycemic index food with a low glycemic index food may have a different effect on blood sugar levels than eating the high glycemic index food alone.
3. Can be confusing: Understanding the glycemic index can be challenging, and it may not be practical to follow a strict glycemic index diet.
In conclusion, the glycemic index can be a useful tool for managing blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, improving heart health, and aiding in weight loss. However, it is important to remember that it has limitations and should be used in conjunction with other dietary guidelines.
As a journalist, it is my responsibility to provide accurate information to my readers. Today, we will be discussing the glycemic index. The glycemic index is a ranking system that measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raises blood sugar levels. High glycemic index foods raise blood sugar levels rapidly, while low glycemic index foods have a slower effect. Understanding the glycemic index can help you make informed decisions about which foods to include in your diet.
Low glycemic index foods are typically healthier choices because they provide sustained energy and help control hunger. Foods with a low glycemic index score include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. On the other hand, high glycemic index foods like white bread, sugary drinks, and sweets can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and are associated with an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
It is important to note that the glycemic index should not be the sole factor in making food choices. Other factors such as nutrient content, portion size, and overall dietary pattern should also be considered. However, understanding the glycemic index can be a helpful tool in managing blood sugar levels and promoting overall health. So next time you are deciding what to eat, consider the glycemic index and make a choice that will benefit your body in the long run.
In conclusion, the glycemic index is a valuable tool in understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels. Incorporating low glycemic index foods into your diet can promote sustained energy and help control hunger. While the glycemic index should not be the only factor in making food choices, it is important to consider when striving for optimal health. I encourage you to do your own research and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best dietary plan for you.
Video glycemic index
Visit VideoPeople also ask about glycemic index1. What is the glycemic index?The glycemic index (GI) is a ranking system that rates carbohydrates based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels.2. Why is the glycemic index important?The GI can be useful for managing blood sugar levels, especially for people with diabetes. It can also help with weight management and overall health.3. What foods have a high glycemic index?Foods that have a high GI include white bread, white rice, potatoes, sugary drinks, and processed snacks.4. What foods have a low glycemic index?Foods that have a low GI include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds.5. Is the glycemic index the only factor to consider when choosing what to eat?No, the GI is just one factor to consider. It’s important to also look at the overall nutrient content of a food, including its fiber, protein, and fat content.6. Can the glycemic index vary depending on how a food is prepared or cooked?Yes, cooking and processing can affect the GI of certain foods. For example, overcooking pasta can increase its GI, while adding vinegar to a meal can lower its GI.7. Should everyone follow a low glycemic index diet?No, not necessarily. The GI is just one tool for managing blood sugar levels and overall health, and it may not be appropriate for everyone. It’s best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice.






