
Dairy allergy is a reaction to milk proteins, causing symptoms ranging from mild rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
It’s that time of year again when pumpkin spice lattes and warm apple cider are on every menu. However, for individuals with a dairy allergy, indulging in these seasonal treats can result in a trip to the emergency room. With approximately 65% of the world’s population being lactose intolerant, it’s no surprise that dairy allergies are becoming more common. Not only can a dairy allergy cause uncomfortable symptoms such as stomach pain and bloating, but it can also lead to life-threatening anaphylaxis. It’s crucial for individuals with a dairy allergy to be vigilant when it comes to reading food labels and asking restaurants about their ingredients. Let’s take a closer look at what a dairy allergy entails and how it can impact one’s daily life.
Daftar Isi
The Rise of Dairy Allergies
Dairy allergies have become increasingly common in recent years, affecting an estimated 2-3% of children and adults. This rise in dairy allergies has left many people wondering why this is happening and what they can do to manage this condition.
What is a Dairy Allergy?
A dairy allergy is a reaction that occurs when the immune system identifies the proteins found in milk and other dairy products as harmful invaders. The body then produces antibodies to fight off these proteins, triggering an allergic reaction. Symptoms may range from mild to severe and can include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, and stomach pain.
Distinguishing Dairy Allergy from Lactose Intolerance
It is important to note that a dairy allergy is different from lactose intolerance, which is the inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and milk products. Lactose intolerance may cause similar symptoms, but it is not life-threatening and does not involve the immune system.
The Causes of Dairy Allergies
Genetics and Family History
Research suggests that genetics may play a role in the development of dairy allergies. Children with a family history of allergies are more likely to develop a dairy allergy themselves.
Exposure to Cow’s Milk Protein
Some experts believe that early exposure to cow’s milk protein, either through direct consumption or breastfeeding, may increase the risk of developing a dairy allergy. Introducing cow’s milk to infants before six months of age may also increase the risk.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as pollution and exposure to certain chemicals, may also contribute to the development of dairy allergies. However, more research is needed to fully understand the connection between these factors and dairy allergies.
Managing a Dairy Allergy
Dietary Changes
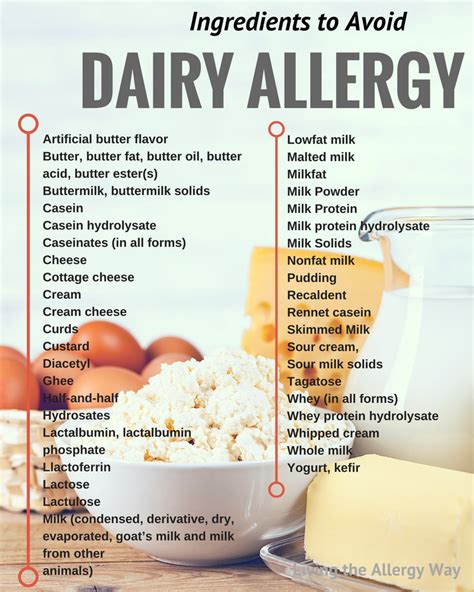
The most effective way to manage a dairy allergy is to avoid all dairy products, including milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. Fortunately, there are many dairy-free alternatives available, such as soy milk, almond milk, and coconut milk. It is important to read food labels carefully, as dairy may be found in unexpected places, such as salad dressings and baked goods.
Medications
In cases of severe dairy allergies, medications such as epinephrine may be prescribed to be used in emergency situations. Antihistamines may also be used to relieve mild symptoms such as itching and hives.
Conclusion
Dairy allergies can be challenging to manage, but with the right tools and support, those affected can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. By understanding the causes and symptoms of dairy allergies, and making necessary dietary changes, individuals can take control of their health and well-being.
What is a Dairy Allergy?A dairy allergy is a type of food allergy that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies proteins in milk and other dairy products as harmful and triggers an allergic reaction. This immune response can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, including hives, stomach cramps, vomiting, and difficulty breathing. While dairy allergy can occur at any age, it is most common in children, affecting one out of every 50 infants.Symptoms of Dairy AllergyThe symptoms of dairy allergy can vary from person to person and can appear within a few minutes to several hours after consuming dairy products. Common symptoms include hives, itching, swelling, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting. In severe cases, individuals may experience anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction that can cause difficulty breathing, a drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms after consuming dairy products, seek immediate medical attention.How is Dairy Allergy Diagnosed?A dairy allergy can be diagnosed through allergy testing, which involves a skin prick test or a blood test. These tests can determine whether the immune system has produced antibodies to milk proteins. Another diagnostic method is an elimination diet, where all dairy products are removed from the diet for a period of time, and then gradually reintroduced to observe any allergic reactions. It is important to note that self-diagnosis or avoidance of dairy products without proper diagnosis can lead to nutritional deficiencies.The Difference Between Dairy Allergy and Lactose IntoleranceDairy allergy and lactose intolerance are often confused, but they are not the same thing. While a dairy allergy is an immune response to the proteins in milk, lactose intolerance is a digestive issue where the body cannot digest lactose, a sugar found in milk. Symptoms of lactose intolerance include bloating, gas, and diarrhea, but do not involve the immune system. It is important to differentiate between these two conditions as they require different treatments.Treatment for Dairy AllergyThe primary treatment for dairy allergy is to avoid all dairy products. This can be challenging as dairy is a common ingredient in many foods, including baked goods, processed foods, and sauces. It is important to read food labels carefully and to inform restaurants of the allergy when dining out. In cases of acute allergic reactions, antihistamines or epinephrine auto-injectors may be prescribed. It is important to carry an auto-injector at all times if you have a history of severe allergic reactions.Dairy-Free AlternativesIndividuals with dairy allergy can still enjoy a diverse and nutritious diet by substituting dairy products with plant-based alternatives such as soy milk, almond milk, and coconut milk. There are also many dairy-free cheese, yogurt, and ice cream options available. These alternatives can provide the same nutritional benefits as dairy products, including calcium, vitamin D, and protein.Potential Complications of a Dairy AllergyIf left untreated, a dairy allergy can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Anaphylaxis can cause difficulty breathing, a drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of anaphylaxis after consuming dairy products.Dairy Allergy in ChildrenDairy allergy is one of the most common allergies in children, affecting one out of every 50 infants. Children may outgrow the allergy as they get older, but it can persist into adulthood. It is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of dairy allergy and to inform schools and daycare centers of the child’s allergy. Children with dairy allergy can still enjoy a nutritious and balanced diet with the help of a healthcare professional.Dairy Allergy PreventionThere is no known way to prevent a dairy allergy from developing, but exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life can help to reduce the risk. If you have a family history of food allergies, talk to your healthcare provider about introducing allergenic foods to your child’s diet.Coping with Dairy AllergyLiving with a dairy allergy can be challenging, but with proper education and support, individuals can learn to manage their allergy and continue to enjoy a healthy and balanced diet. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a safe and nutritious meal plan and to inform friends, family, and coworkers of the allergy. There are also support groups and resources available to help individuals cope with dairy allergy and other food allergies.Dairy Allergy: Pros and ConsAs a journalist, it is important to provide information that can help people make informed decisions. When it comes to dairy allergy, there are pros and cons that should be considered.Pros:1. Improved Digestion: People with dairy allergy may experience improved digestion when they eliminate dairy products from their diet. Symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea can be reduced or eliminated.2. Reduced Inflammation: Dairy products contain a protein called casein which can cause inflammation in the body. By avoiding dairy products, people with dairy allergy can reduce inflammation which can lead to improved overall health.3. Weight Loss: Many dairy products are high in fat and calories. Avoiding these products can lead to weight loss, which can have a positive impact on overall health.Cons:1. Nutrient Deficiencies: Dairy products are a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients. Eliminating these products from the diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies which can have negative health consequences.2. Limited Food Choices: Many foods contain dairy products. Eliminating dairy products from the diet can limit food choices, making it more difficult to follow a balanced diet.3. Social Issues: Avoiding dairy products can be challenging in social situations. Dining out or attending events where food is served can be difficult, and people with dairy allergy may feel left out or isolated.In conclusion, while there are pros and cons to eliminating dairy products from the diet, it is important for people with dairy allergy to weigh these factors and make an informed decision about their dietary choices.
As a journalist, it is my duty to inform you about the dangers of dairy allergies and how to manage them. Dairy allergy is an adverse reaction to the proteins found in cow’s milk, which can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe. This condition affects millions of people worldwide, and it is essential to understand its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
The symptoms of dairy allergy can range from mild to severe and can occur within minutes or hours after consuming dairy products. The most common symptoms include hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, difficulty breathing, stomach cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. If you suspect that you or your loved one has a dairy allergy, it is crucial to seek medical advice and avoid all dairy products.
The management of dairy allergy involves avoiding all dairy products and finding alternative sources of calcium and other essential nutrients. There are many dairy-free alternatives available in the market, such as soy milk, almond milk, coconut milk, and rice milk, among others. It is vital to read food labels carefully, as dairy products can be hidden in many processed foods. Additionally, it is advisable to carry an epinephrine auto-injector at all times, especially if you have a severe dairy allergy. This device can quickly deliver a life-saving dose of epinephrine in case of an allergic reaction.
In conclusion, dairy allergy is a serious condition that requires proper management to avoid potentially life-threatening reactions. If you suspect that you or your loved one has a dairy allergy, seek medical advice and avoid all dairy products. Remember to read food labels carefully and find alternative sources of calcium and other essential nutrients. By taking these precautions, you can live a healthy and fulfilling life, free from the dangers of dairy allergy.
Visit VideoPeople Also Ask: Dairy Allergy1. What is a dairy allergy?A dairy allergy is a condition in which a person’s immune system overreacts to proteins found in dairy products. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild itching and hives to more severe reactions such as difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.2. What are the symptoms of a dairy allergy?Symptoms of a dairy allergy can include hives, itching, swelling, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, anaphylaxis can occur, which is a life-threatening reaction that requires immediate medical attention.3. How is a dairy allergy diagnosed?A dairy allergy is typically diagnosed through skin prick tests, blood tests, and elimination diets. Your doctor may also perform a food challenge test to confirm the diagnosis.4. Can a dairy allergy be treated?There is no cure for a dairy allergy, but symptoms can be managed through avoidance of dairy products and the use of medications such as antihistamines and epinephrine.5. What foods should I avoid if I have a dairy allergy?If you have a dairy allergy, you should avoid all foods that contain milk or milk products, including cheese, yogurt, butter, cream, and ice cream. You should also check food labels carefully for hidden sources of dairy, such as whey, casein, and lactose.






