
Carbon trading in Indonesia helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions while generating revenue. Learn about the country’s carbon market and policies.
Carbon trading is a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by incentivizing companies and nations to limit their carbon footprint. Indonesia, one of the world’s largest emitters of carbon dioxide, has implemented its own carbon trading scheme in an effort to combat climate change. This innovative approach to environmental policy has garnered attention from around the world, and its success could have profound implications for the future of sustainable development.
At the heart of Indonesia’s carbon trading scheme is the concept of carbon credits. These credits represent a metric ton of carbon dioxide that has been mitigated or removed from the atmosphere. Companies and nations can purchase these credits to offset their own emissions, thereby reducing their overall carbon footprint. The idea is to create a market-based incentive for reducing carbon emissions, with the hope that this will spur innovation and investment in cleaner energy technologies.
Despite some initial challenges, Indonesia’s carbon trading scheme has already shown promise. By 2020, the country had reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by almost 13% compared to business as usual levels. The government has also pledged to reduce emissions by 29% by 2030, indicating a strong commitment to tackling climate change. As the world continues to grapple with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, Indonesia’s carbon trading scheme may provide a model for other nations to follow.
Daftar Isi
Introduction
Carbon trading has become an increasingly popular mechanism to combat climate change in recent years. In Indonesia, carbon trading has been gaining traction as the government seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while promoting economic growth. This article will explore the current state of carbon trading in Indonesia and its potential future.
What is Carbon Trading?
Carbon trading is a market-based mechanism that allows countries or companies to purchase and sell carbon credits. Carbon credits are awarded to entities that reduce their greenhouse gas emissions below a certain level, and then can be sold to other entities that need to offset their own emissions. Carbon trading is seen as a cost-effective way to reduce emissions while promoting economic growth.
The Status of Carbon Trading in Indonesia
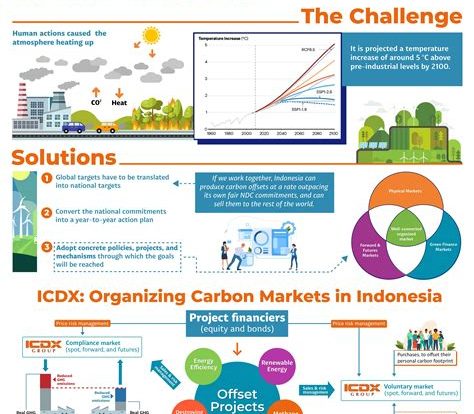
Indonesia is the world’s third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases, largely due to deforestation and land-use change. The country has committed to reducing its emissions by 29% by 2030, and carbon trading is seen as a key tool to achieve this goal. The government has implemented several initiatives to promote carbon trading in the country, such as the establishment of the Indonesia Domestic Emissions Trading Scheme (ID-ETS) in 2018.
ID-ETS
The ID-ETS is a voluntary program that allows companies to trade carbon credits domestically. Companies that reduce their emissions can sell their credits to other companies that need to offset their own emissions. The program is currently in a pilot phase, with several companies participating. However, the government hopes to expand the program in the coming years.
REDD+
Another initiative to promote carbon trading in Indonesia is the Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) program. This program aims to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation by providing incentives for forest conservation. Carbon credits can be awarded to communities or companies that protect forests, which can then be sold to other entities. The program has been implemented in several provinces in Indonesia, with varying degrees of success.
Challenges and Opportunities
While carbon trading has potential to reduce emissions and promote economic growth in Indonesia, there are several challenges that must be addressed. One major challenge is the lack of infrastructure and expertise to implement carbon trading programs effectively. Additionally, corruption and lack of transparency could hinder the effectiveness of these programs.
Opportunities for Growth
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for growth in the carbon trading market in Indonesia. The country’s vast forests provide ample opportunities for the REDD+ program, and the government’s commitment to reducing emissions provides a strong foundation for the ID-ETS program. Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable products and services could drive demand for carbon credits.
Conclusion
Carbon trading has the potential to play a significant role in reducing emissions and promoting economic growth in Indonesia. While there are challenges to overcome, the government’s commitment to reducing emissions and the country’s vast natural resources provide opportunities for growth in the carbon trading market. As the world continues to grapple with climate change, carbon trading will likely become an increasingly important tool in the fight against greenhouse gas emissions.
Introduction: Understanding the Concept of Carbon Trading and its Relevance in Indonesia
Carbon trading is a market-based mechanism aimed at mitigating climate change by providing incentives for companies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In recent years, the concept has gained popularity globally as a means of promoting sustainable practices. In Indonesia, carbon trading has been implemented to reduce emissions and encourage green investments. This article explores Indonesia’s role in global carbon trading, its carbon trading framework, mechanisms, benefits, challenges, successful projects, potential for REDD+ mechanisms, and outlook for the future.
The Role of Indonesia in Global Carbon Trading
As one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in the world, Indonesia has a critical role to play in global carbon trading. Its vast forests and extensive agricultural sector offer immense potential for reducing emissions through sustainable land use policies and conservation initiatives. By participating in carbon trading, Indonesia can contribute to the global effort to mitigate climate change while also promoting sustainable development.
Indonesia’s Carbon Trading Framework
Indonesia’s carbon trading framework provides a regulatory framework for companies to participate in emissions trading. This framework includes provisions for monitoring, reporting, and verification of emissions, while also addressing issues related to offsets and carbon credits. The framework aims to promote transparency, accountability, and integrity in the carbon trading market.
Mechanisms for Carbon Trading in Indonesia
Indonesia has adopted several mechanisms for carbon trading, including the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) and the Joint Implementation (JI) approach. These mechanisms allow companies to earn carbon credits by reducing emissions through sustainable practices. The CDM allows companies to undertake emission reduction projects in non-Annex I countries, while the JI approach allows companies to undertake emission reduction projects in other Annex I countries.
The Benefits of Carbon Trading for Indonesia
Carbon trading provides several benefits for Indonesia, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable practices, and encouraging investment in clean technologies and renewable energy. By participating in carbon trading, Indonesia can attract green investments and promote sustainable development.
Challenges Faced by Indonesia in Implementing Carbon Trading
Despite the potential benefits of carbon trading, Indonesia faces several challenges in implementing these mechanisms. These challenges include the lack of a robust legal and regulatory framework, limited public awareness, and a lack of capacity for monitoring and verification. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring the effective implementation of carbon trading mechanisms in Indonesia.
Successful Carbon Trading Projects in Indonesia
Several successful carbon trading projects have been implemented in Indonesia, including the Rimba Raya Biodiversity Reserve Project and the Kalimantan Forest and Climate Partnership. These projects have reduced greenhouse gas emissions and contributed to sustainable development in local communities. Such projects demonstrate the potential of carbon trading to promote sustainable development while mitigating climate change.
Indonesia’s Potential for REDD+ Mechanisms
Indonesia has significant potential for reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD+) through sustainable land use policies and conservation initiatives. These mechanisms can provide opportunities for carbon trading while also promoting biodiversity and supporting local communities. Indonesia’s potential for REDD+ mechanisms underscores the importance of integrating carbon trading into broader sustainable development goals.
Outlook for Carbon Trading in Indonesia
The outlook for carbon trading in Indonesia is positive, with the potential for new projects and initiatives in the coming years. Continued efforts will be needed to overcome the challenges faced by Indonesia and ensure the effective implementation of carbon trading mechanisms. However, the potential benefits of carbon trading for Indonesia’s sustainable development make it a promising strategy for mitigating climate change.
Conclusion: The Importance of Carbon Trading for Indonesia’s Sustainable Development
Carbon trading can play a critical role in Indonesia’s efforts to mitigate climate change and promote sustainable development. By implementing effective carbon trading mechanisms, Indonesia can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable practices, and support the transition to a low-carbon economy. The challenges faced by Indonesia in implementing carbon trading should not deter its efforts to adopt this market-based mechanism. By working towards overcoming these challenges, Indonesia can contribute to the global effort to mitigate climate change while promoting sustainable development.Carbon trading in Indonesia: A mixed bag of pros and cons
Carbon trading has gained prominence in the global climate change discourse as a means to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Indonesia, as one of the world’s largest emitters of carbon dioxide, has also embraced the concept of carbon trading as a way to mitigate the impacts of climate change. However, the implementation of carbon trading in Indonesia has been met with mixed reactions from various stakeholders.
Pros of Carbon Trading in Indonesia
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: Carbon trading can incentivize companies to reduce their carbon footprint by limiting their emissions or investing in cleaner technologies.
- Generating revenue: By participating in carbon trading, companies can earn credits that can be sold on the global market, providing an additional revenue stream.
- Encouraging sustainable practices: Carbon trading can encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices, such as reforestation or using renewable energy sources, which can have positive environmental and social impacts.
Cons of Carbon Trading in Indonesia
- Lack of transparency: There have been concerns about the lack of transparency in the carbon trading market in Indonesia, with some companies accused of inflating their emissions reduction figures.
- Difficulty in verifying carbon offsets: Verifying the validity of carbon offsets can be challenging, which can lead to the overestimation of emissions reductions and undermine the effectiveness of carbon trading.
- Potential for market manipulation: There is a risk of market manipulation by large corporations, which could lead to a concentration of carbon credits in the hands of a few players, making it difficult for smaller companies to participate in the market.
Overall, while carbon trading can offer significant benefits in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and generating revenue, it is important to address the potential drawbacks to ensure the integrity and effectiveness of the system. Transparency, accountability, and verification mechanisms must be put in place to prevent market manipulation and ensure that carbon trading contributes to sustainable development.
As the world is trying to find solutions to the rising global temperatures, Indonesia has taken a step towards tackling climate change by implementing carbon trading. This system enables companies to buy and sell permits to emit carbon dioxide. It is a market-based approach that incentivizes businesses to reduce their carbon emissions while creating opportunities for investment in low-carbon technologies.
Indonesia has become the first country in Southeast Asia to begin carbon trading. The government has set a target of reducing carbon emissions by 29% by 2030. The implementation of this system has been welcomed by businesses who see it as an opportunity to reduce their carbon footprint while also improving their bottom line. The carbon trading system will contribute to the country’s efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help the nation achieve its climate goals.
However, there are concerns about the effectiveness of the system. Some experts argue that carbon trading may not be the most effective way to reduce emissions as it does not address the root cause of the problem. They believe that a more comprehensive approach, such as a carbon tax, would be more effective in reducing emissions. Nevertheless, carbon trading is a step towards a low-carbon economy, and it is important for businesses to participate in this initiative to help reduce their environmental impact.
In conclusion, carbon trading is an important step towards a low-carbon economy in Indonesia. While it may not be perfect, it is a significant step towards reducing the country’s carbon emissions and achieving its climate goals. As individuals and businesses, we must take responsibility for our impact on the environment and actively seek ways to reduce our carbon footprint. By participating in initiatives such as carbon trading, we can make a positive impact on the environment and create a more sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.
Video carbon trading indonesia
Carbon trading in Indonesia has been a hot topic in recent years, with many people asking questions about how it works and its impact on the environment. Here are some of the most common questions people ask about carbon trading in Indonesia:
- What is carbon trading?
Carbon trading is a system that allows companies to buy and sell carbon credits, which represent a certain amount of carbon dioxide emissions. Companies that emit less than their allotted amount of carbon dioxide can sell their extra credits to companies that emit more than they are allowed. This creates a financial incentive for companies to reduce their carbon emissions. - How does carbon trading work in Indonesia?
In Indonesia, carbon trading is primarily focused on the forestry sector. The country has one of the highest rates of deforestation in the world, and carbon trading is seen as a way to incentivize companies and communities to protect forests and reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. - Who benefits from carbon trading in Indonesia?
The primary beneficiaries of carbon trading in Indonesia are companies and communities that are able to reduce their carbon emissions and generate carbon credits. These credits can then be sold to companies that need them to offset their own emissions. The Indonesian government also benefits by receiving revenue from the sale of carbon credits. - What are the challenges of carbon trading in Indonesia?
One of the biggest challenges of carbon trading in Indonesia is ensuring that the credits being generated are legitimate and represent real emissions reductions. There have been cases of fraudulent carbon credits being sold in the past, which has led to a lack of trust in the system. Additionally, there are concerns about the impact of carbon trading on local communities and whether they are being adequately compensated for their participation. - What is the future of carbon trading in Indonesia?
The future of carbon trading in Indonesia is uncertain, as the country has yet to fully embrace the system. However, there is growing interest from companies and government agencies in exploring carbon trading as a way to reduce emissions and protect forests. With the right policies and safeguards in place, carbon trading could play an important role in Indonesia’s efforts to address climate change.






